Water Softeners - What Are They and How Do They Work?

Many American families have a water softener in their homes. In fact, 85% of Americans have hard water, while only 25% of households report having a water softener installed. From mildly inconvenient to plumbing and appliance ruining, hard water can have a lasting impact on you and your home. If you have well water, then you know that almost every house with well water has hard water.
What Is Hard Water?
Whether water is hard or not is dependent on the presence of two water-soluble minerals, namely Magnesium and Calcium. In the US total hardness (TH) is commonly measured in milligrams per liter (mg/l) or grains per gallon (gpg). That being said, measuring total hardness means measuring calcium and magnesium carbonate which is the concentration of dissolved calcium and magnesium in the water supply. One ppm means that one unit of calcium carbonate is dissolved in one million units of water. GPG is used exclusively for hardness measurements, 1 gpg is equal to 17.1 mg/l or ppm (ppm and mg/l are the same measurement). The table below shows the measurements for each classification of water hardness.
| Term | Grains Per Gallon (GPG) | PPM (MG/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Soft | < 1.0 | <17.0 |
| Slightly Hard | 1.0 - 3.5 | 17.1 - 60 |
| Moderately Hard | 3.5 - 7.0 | 60 - 120 |
| Hard | 7.0 - 10.5 | 120 - 180 |
| Very Hard | > 10.5 | > 180 |
Learn more about Hard Water
How Do I Know If My Water Is Hard?
One of the telltale signs of hard water is spotty dishes and glassware. You may also notice a film of soap scum developing on your shower walls, shower doors, or bathtub (soap easily combines with dissolved solids to form a difficult to remove film.). Your laundry might start to look dingier than you remember since hard water often interferes with cleaning agents. Your skin may feel scratchy and rough, especially during the winter months when humidity is low.

Effects of Hard Water
Some of the effects of hard water are easily detected, while others remain hidden until they create costly repairs. Hard water deposits scale and this scale build-up will affect the performance of your household appliances. When hard water is heated, dissolved solids settle out of suspension. These precipitates form a mineral deposit that builds up in the bottom of your water heater, shortening its lifespan and increasing the energy required to heat your water. This scale also accumulates inside your pipes, washing machines, refrigerators, dishwashers, and coffee pots, eventually blocking the flow of water.
Is it worth installing a water softener?
When you take into consideration the benefits that salt-based water softeners provide, it's easy to see that installing a salt-based water softener is a worthwhile investment. The issues that are caused by hard water can lead to some expensive repairs. Salt based water softeners are the key to removing minerals in the water that can cause all types of issues.
Is It Safe To Drink Soft Water?
Sheldon G. Sheps, M.D. of MayoClinic.org states,
Regular tap water contains very little sodium. The amount of sodium a water softener adds to tap water depends on the "hardness" of the water. Hard water contains large amounts of calcium and magnesium. Some water-softening systems replace calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions. The higher the concentration of calcium and magnesium, the more sodium needed to soften the water. Even so, the added sodium doesn't add up to much.
An 8-ounce (237-milliliter) glass of softened water generally contains less than 12.5 milligrams of sodium, which is well within the Food and Drug Administration's definition of "very low sodium." Thus, it's unlikely that sodium in softened water would pose a risk for most healthy people. However, if you're on a very low-sodium diet and you're concerned about the amount of sodium in softened water, you may want to consider a water-purification system that uses potassium chloride instead. Another option is to soften only the hot water and
use unsoftened cold water for drinking and cooking. In any case, it's important to keep in mind that the majority of sodium in an average person's diet comes from table salt and processed foods. Thus, the best way to decrease sodium in your diet is by putting away the saltshaker and cutting back on processed foods.
If you are worried about sodium in your drinking water, you can easily solve the problem by installing an under sink reverse osmosis system. By doing this you remove the salt as well as a multitude of other harmful contaminants.
What Is A Water Softener?
A water softener is typically described as a device that removes Calcium (Ca2+) and Magnesium (Mg2+) from a water supply turning hard water into soft water. Modern water softeners use a process called Ion Exchange to remove the calcium and magnesium ions and replace them with sodium ions.
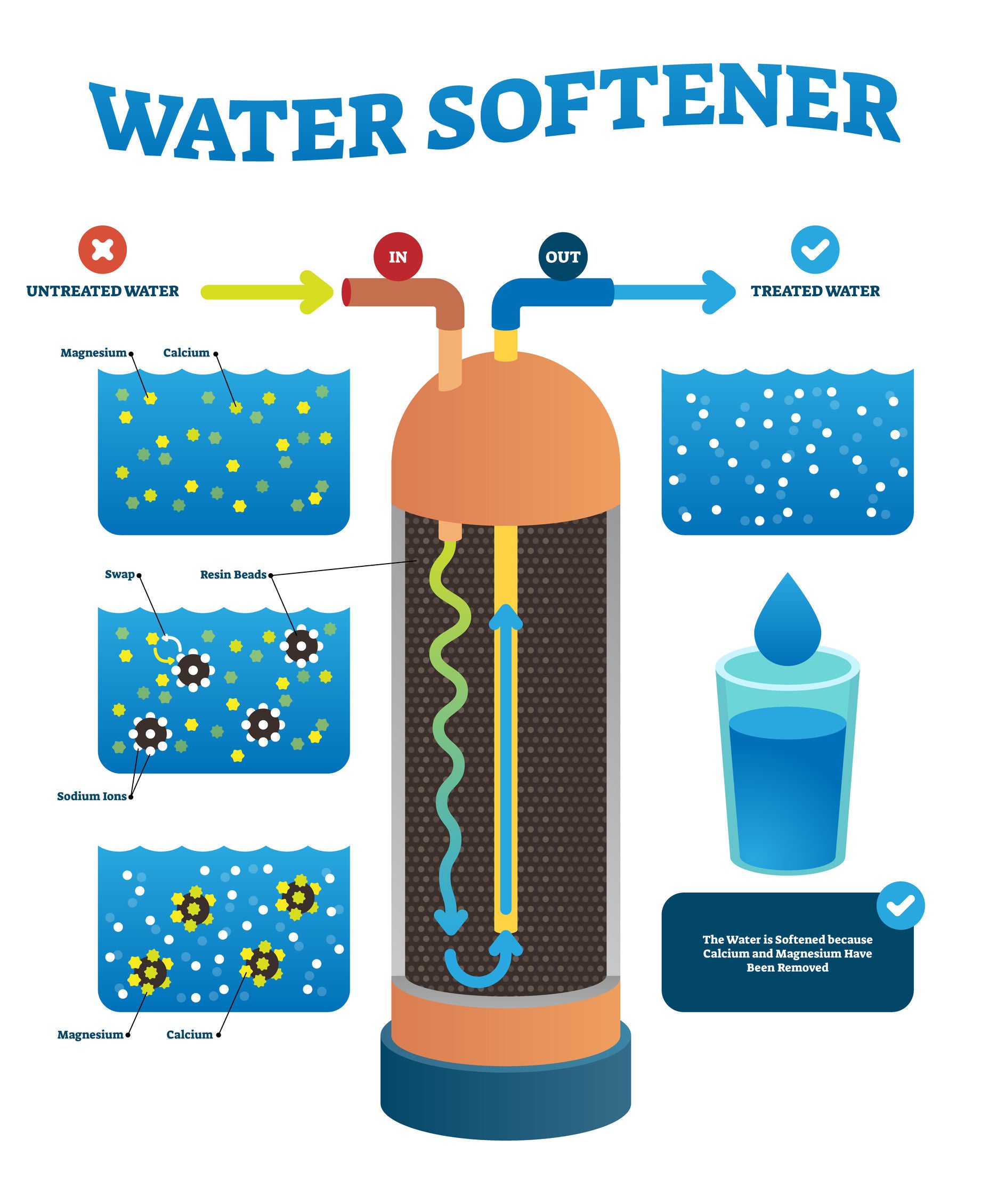
How Do Salt Based Water Softeners work?
Water Softeners remove hard water minerals by using ion exchange. In this exchange the hard water minerals trade position with sodium ions that are weakly bound to the water softener resin. The resin is cleaned during regeneration when brine water is back flowed into the main tank from the brine tank.
- Step 1 - Hard water flows into the water softener.
- Step 2 - The positive ions Calcium (Ca2+) and Magnesium (Mg2+) are attracted to and trapped by the sodium-charged resin beads. As the hard water minerals bind to the resin they displace the weakly bonded sodium ions. - they basically switch places.
- Step 3 - Soft water flows into your home.
A Closer Look At Ion Exchange
- Step 1 - Resin beads hold sodium.
- Step 2 - Hard water flows through the resin beads
- Step 3 - Sodium is swapped for hard water minerals and soft water is produced

How To Properly Size A Water Softener?
Traditionally, water softeners have been sized using the following formula:
- Step 1 - Enter the hardness in gpg (grains per gallon);
- Step 2 - Enter the iron in ppm (parts per million) multiplied by 4;
- Step 3 - Enter the manganese in ppm multiplied by 6;
- Step 4 - Add Steps 1-3 to get what is called Compensated Hardness;
- Step 5 - Multiply the number in the family by 75 to 100 gallons (that's how much water the average person uses a day)
- Step 6 - Multiply Step 4 times Step 5 and that gives you the total grain capacity you need each day
In this equation, an arbitrary number is assigned to both iron and manganese as a factor which is added to the actual hardness to determine how much hardness was in each gallon of water. From here, you need to figure out how many gallons of water you used each day and multiplied that by the hardness of each gallon. This will give you how many grains of hardness need to be removed from the water to make it soft. You can then decide how often you want to regenerate (usually 2-4 days between regenerations) and you can pick a softener in that size range. This is the equation that most companies use to determine water softener size.
Here's the issue -Sure with a softener sized this way, you'll have enough capacity to soften hundreds of gallons a day. However, you also need to account for how many water fixtures are fed by your water softener. If you don't then you will not have enough hourly capacity to continuously feed soft water to all your water fixtures. Contrary to popular belief, you can pull water through a water softener faster than it can soften. Essentially you overwhelm the resin with a high flow through and create what is called hardness leakage. If the water does not have enough contact time, actually prolonged-contact time, then it will be wet, but it may not be soft. Hardness leakage allows hard water through your softener, which pretty much defeats the purpose of having one, don't you think?
The Solution
Buy a bigger softener. Take your answer from the above equation and purchase the next size up. On average it costs about $100 more to upsize a water softener and increase the grain count. With a slightly oversized water softener you will have a water softening system that needs to regenerate less since it has a higher capacity, this leads to less salt usage, less water waste, and additional savings. Plus you never run out of soft water.

The Evolution of Water Softeners
Water softeners have been around for nearly one hundred years. It was allegedly in 1924, that Emmett J. Culligan invented a water softener control valve and started his water softening business. Wikipedia says that it was 1936, but what's 14 years among friends? Thank you Mr. Culligan!
Manual Salt Based Water Softeners
The very first softener valves were of the manual variety. That meant that you had to manually initiate regeneration and pretty much babysit the systems for a couple of hours while the softener regenerated (recharged) itself using the brine tank. That was pretty inconvenient, so there was a need for automation.
Automatic Time-Clock Salt Based Water Softeners
The manual water softener was replaced by a time-clock controlled water softener. It allowed you to choose on how many days of the week it should regenerate. Regeneration was generally accomplished at 2:00 AM when no one would typically be using water. All you had to do was set the time of day and pick the days it needed to regenerate and you had an automatic time-clock controlled water softener.
Metered (Demand) Salt Based Water Softeners
The Automatic Time-Clock Water Softener served a purpose and had a great run, but water usage can vary from day-to-day and the day of the week is not nearly as important as the gallons used. It is very common for families to wash multiple loads of laundry and use a lot more water on the weekend. Another opportunity for innovation: The demand or meter-controlled water softener was born. It was probably in the late 1970's or early 1980's that they became commercialized. Instead of regenerating based upon the day of the week, they regenerated based upon the gallons used. That was a big leap forward.
It makes perfect sense to regenerate based upon the number of gallons used because there is a finite number of gallons that can pass through a water softener before it needs to regenerate. The meter-controlled water softener saved both salt and water and to this day, nearly all water softeners that are sold are of the meter-controlled variety.
Twin-Tank Meter-Controlled Salt Based Water Softeners
In 1970, Bill Prior and Jim Kewley pioneered the development of a non-electric, meter-controlled twin-alternating water softener. Their company was Kinetico and they revolutionized the water softening business with their twin-tank design. Bill Prior has since passed away and the company has been sold to Axel Johnson, but they are still a very large company that uses the direct in-home method of sales. The invention of Kinetico spawned many imitators and frankly, in the computer age, what added value is there to a non-electric water softener? It might save you a dollar or two of electricity a year. Nearly, every water softener company now has a twin-tank meter-controlled system.
Advanced Smartphone Electronics
Obviously, with the advancement in technology, the computerization of water softeners was bound to come, making them highly efficient and virtually trouble-free. Would you have a non-electric computer? Then why a non-electric water softener? You lose a lot of features without smart electronics. Most water softeners controlled by a smartphone can be precision-tuned to be highly efficient in salt and wastewater usage and they record historical data such as gallons per day, peak water flow, and historical water usage.

Is It Hard To Install A Water Softener?
Water softener installations are relatively easy to do, we provide our customers with detailed videos, documentation, and live tech support in case there are any issues installing your water softening system.
Should I Rent or Buy A Water Softener?
For this scenario let's assume that you live in a two-person household with moderately hard water, you are in the market for a 32,000 grain water softener, and are having a hard time deciding if you want to rent a water softener or purchase one. We can assume that you will use about 10lbs of salt per week so a 40 lbs bag of salt should last you one month. Let's calculate the total cost of a rental from one of the biggest suppliers in the country (I'm sure you can guess who) vs buying from Us Water Systems over a 15-year period.
| Cost over 15 years | ||
|---|---|---|
| Item | Rental unit | Owned Unit |
| Purchase Price: Flexx Pro 10 gpm ¾ inch | - | $1095.00 |
| Rental cost over 15 years | ($32 *12months)*15yrs = $5760.00 | - |
| Salt delivery | ($9.12*12months)*15years = $1641.60 | - |
| Diamond Crystal Salt | - | ($4.47*12months)*15years = $804.60 |
| Installation Price | $129.00 | - |
| Total cost over 15 years | $7530.60 | $1899.60 |
How Much Does A Whole House Water Softener cost?
As you can see the cost difference between the two is dramatically different. The cost becomes even greater if you are someone who owns multiple rental properties. If you own 5 rentals and rent a water softener you are looking at a cost of almost $40,000 over a 15-year period. To many people, the thought of installing a water softener can be a bit intimidating. We understand this, that's why we provide our customers with detailed manuals, installation videos, and around the clock tech support. We think that every DIY installation should be as smooth and painless as possible.
So what will you do, rent or buy?
How do I Treat Hard Water In Areas Where Water Softeners Are Banned?
The best way to treat hard water is with a water softener - it actually makes the water soft. That is an undisputed fact. However, a few parts of the country have banned the use of water softeners. If you live in one of these areas and are struggling with hard water then your best bet is to use a salt-free water conditioner. Our salt-free conditioner is called the GreenWave, it uses Filtersorb SP 3 Media derived from German engineering. SP3 utilizes a process called Nucleation Assisted Crystallization or NAC for short to bind hard water minerals.
How it works
As the hard water passes through a pressure vessel (in the upflow configuration) the calcium bicarbonate Ca(HCO3)2 is transformed into the aragonite form of calcium carbonate CaCO3
crystals. These crystals are formed through the decomposition and crystallization process, forming very stable harmless crystals.
The following equation describes the reaction that occurs inside the pressure vessel when flow over grains of nucleation.
Ca(HCO3)2 ? CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O
Now that you've learned a thing or two about water softeners, which do you think is the better bet: renting or owning a water softener? Comment below and let us know what other types of water treatment you'd like to learn about.










7 Comments
This is very informative! I’ve been considering getting a water softener for a while now, and this article gave me a better idea of what to look for when deciding. I especially appreciated the comparison of the different types of water softeners and their pros and cons. I’ll definitely be referring back to this article when I’m ready to purchase a water softener. Thanks for sharing!
That hole is an overflow in case the water level in the brine tank is too high. It should be connected to a gravity drain, but if water runs out of that hole, there softener is set improperly or is malfunctioning.
I bought. a townhome last year that had a one year old water softener, I put 4 bags of salt in the salt reservoir. When it does the flush cycle it leaks out the hole up high on the side of the unit. It looks like maybe it should have another hose that should go into the drain pipe in the basement. So I havent been able to use it. I thought maybe I used too much salt, so it didnt have enough space for the water.
Well, it does not soften the water.
I have a citrus cartridge system to soften my water. Then I heard it doesn’t work
The only economical way to remove sodium is by reverse osmosis. It is an iron and cannot be filtered. RO is really the only way to do so. We have RO systems from 50 GPD to 20,000 GPD and everything in-between. We have turnkey whole-house RO systems as well. There is no harm in washing clothes or showering in soft water containing sodium as the levels are very low.
How do i remove the sodium?
Osmosis systems are fine for drinking water. However i dont want sodium in my water for washing my body, my clothes or my dishes. I also use water in my workshop for my hobbies and need high volume sodium free water for my projects. Osmosis systems do not provide enough demand for my projects.
What do soft water systems provide or do that high end filtration systems dont provide?
Leave a comment
Please note, comments need to be approved before they are published.